Measurement of Fluoride in Industrial Wastewater
Industries such as glass manufacturing, aluminum (metal) smelting, semiconductor production, and fertilizer processing generate wastewater with high fluoride concentrations, posing significant environmental and health risks.1
Accurate measurement2 and management of fluoride levels is crucial for regulatory compliance and environmental protection.
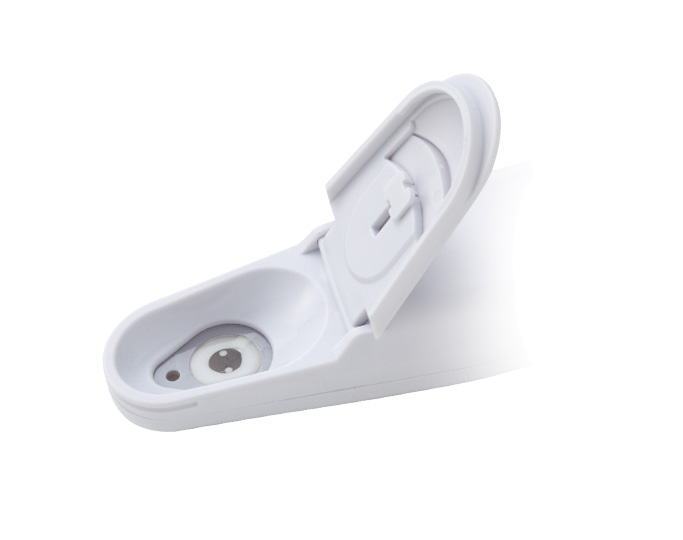
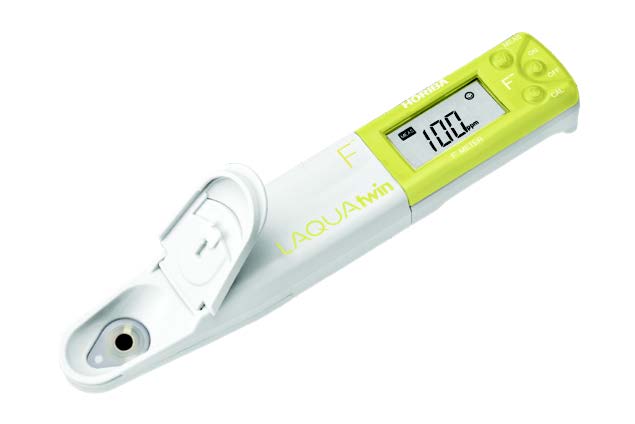
LAQUAtwin F-11 fluoride ion meter provides a reliable, on-site solution for fluoride monitoring, enabling industries to effectively manage and reduce fluoride discharge.




Introduction
Fluoride contamination in industrial wastewater is a significant environmental issue. Industries such as glass manufacturing, aluminium smelting, semiconductor production, and fertilizer processing generate wastewater with high fluoride concentrations. Fluoride, used in these industries can lead to effluents3 containing harmful levels of fluoride if not properly managed.
Excessive fluoride in the environment can cause severe health issues4, including dental and skeletal fluorosis which results in tooth discoloration, enamel damage, and bone deformities. High fluoride exposure may also affect the urinary, renal, endocrine, brain, and reproductive systems.
To meet regulatory standards and mitigate these risks, industries use treatment methods such as adsorption using activated alumina or bone char, membrane processes like reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, chemical precipitation with calcium salts, and electrocoagulation.
Accurate measurement and management of fluoride levels are essential to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and for the protection of public health.
The LAQUAtwin F-11 fluoride ion meter offers a convenient and reliable solution for on-site fluoride measurement, enabling industries to monitor and manage fluoride levels effectively. The meter analyses as little as 0.3ml sample and delivers accurate result in seconds. This rapid test enables industries to adjust their wastewater treatment systems promptly, ensuring compliance with local regulatory discharge limits.
Many countries have stringent environmental regulations that require the industries to ensure that the fluoride concentration in their discharge does not exceed specific limits. Exceeding these limits can result in significant fines and environmental repercussions.
Refer to Table 3 for Fluoride Effluent Limit of Some Countries.
Table 1: Industries with High Fluoride Wastewater
| Industry | Description |
|---|---|
| Glass Manufacturing | Industry uses fluorinated compound (AlF3) to help improve properties of glass, introducing fluoride into wastewater during production processes.5 |
| Aluminium Production | Fluoride is used in the form of cryolite (NaFAlF3) in the electrolytic reduction of alumina to aluminium6, leading to significant fluoride emissions in wastewater. |
| Fertilizer Plants | Phosphate fertilizers contain fluoride7, which can leach into wastewater during production and application. |
| Semiconductor Etching | Etching process use fluoride-containing chemicals8 (HF) to create intricate patterns on silicon wafers. Process generates wastewater with high fluoride concentrations. |
Table 29: Methods for Fluoride Removal
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Adsorption |
Activated Alumina is used to adsorb fluoride ions in water. Bone Charcoal: Charred animal bones are used as catalyst to adsorb fluoride. |
| Membrane Processes |
Reverse Osmosis (RO): The membranes effectively remove ions from wastewater by forcing water through a semi-permeable membrane, leaving fluoride ions behind. Nanofiltration: Similar to RO, nanofiltration membranes can selectively remove fluoride ions from water. |
| Chemical Precipitation | Calcium Salts: Adding calcium salts (calcium chloride) to wastewater can precipitate fluoride as calcium fluoride (CaF2), which can then be removed by sedimentation or filtration. |
| Electrocoagulation | Electrical current is used to coagulate and remove fluoride from wastewater. |
Method
Sample Preparation
Collect a minimum sample (1 ml) of the effluent in the 5ml plastic beaker. Refer to the table below.
| Type of Sample | Does the sample contain Fe3+, Al3+, Si4+ or highly concentrated ions? | |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |
| Two-Point Calibration |
|
Calibrate with 1ppm and 10ppm standard solutions. |
| Measurement | Add 1mL of TISAB & 1mL of sample and measure. | Measure sample directly. |
Calibration
Calibrate the meter with the 1ppm and 10ppm standard solutions provided to ensure accuracy.
Measurement
Place a few drops of the sample on the sensor and wait for a stabilized reading, which will be indicated by ☺.
Recording Results
Record the measurement for compliance and reporting purposes.
Results and Benefits
Using the LAQUAtwin F-11 fluoride ion meter provides several benefits:
- Immediate Results: Obtain fluoride concentration readings onsite without delays, enabling prompt decision-making.
- Compliance Assurance: Ensure that effluent discharge meets regulatory standards, avoiding fines and environmental penalties.
- Portability: The compact and portable design of the meter allows easy on-site testing, making it convenient for use in various locations within the facility.
By implementing the LAQUAtwin F-11 fluoride ion meter, companies can efficiently manage their fluoride discharge, ensuring compliance with environmental standards and avoiding potential fines.
Table 3: Fluoride Effluent Limit of Some Countries
| Country | Fluoride Effluent Limit (ppm / mg/L) |
|---|---|
| Singapore | 15.010 |
| Malaysia |
2.0 (Standard A*), 5.0 (Standard B**)11 *Any inland waters within catchment areas. **Any other inland waters or Malaysian waters. |
| India | Fluoride in effluent is 2.0 mg/L for inland surface water and 15 mg/L for marine coastal areas12 |
Standard A: This standard applies to the discharge of effluents into any inland waters within catchment areas. The limits are stricter to protect sensitive water bodies and ecosystems.
Standard B: This standard applies to the discharge of effluents into any other inland waters or Malaysian waters. The limits are less stringent compared to Standard A.
References and Suggested Readings
- Ahmad, S., Singh, R., Arfin, T., & Neeti, K. (2022, September 28). Fluoride contamination, consequences and removal techniques in water: A Review. Environmental Science: Advances. Retrieved from https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/va/d1va00039j
- Khatkar, R., & Nagpal, S. (2023, January 24). Conventional and advanced detection approaches of fluoride in water: A review - environmental monitoring and assessment. SpringerLink. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10661-022-10888-x#Fig1
- Sinharoy, A., & Chung, C. M. Fluoride removal from wastewater and potential for resource recovery: Comparative studies between different treatment technologies. Environmental Engineering Research. Retrieved from https://www.eeer.org/journal/view.php?number=1574
- Tao, W., Huo, Q., Li, Y., Gu, J., Nie, Y., Li, J., Liu, H., Sawangjang, B., Abdul-Wahab, S., Dong, L., Wang, C., … Xiangyang, M. (2024, August 12). Evaluation of fluoride emissions and pollution from an electrolytic aluminum plant located in Yunnan Province. Journal of Hazardous Materials. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S030438942402079X
- Diwani, G. E., Amin, Sh. K., Attia, N. K., & Hawash, S.I. (2022a, May 18). Fluoride pollutants removal from industrial wastewater - bulletin of the National Research Centre. SpringerOpen. Retrieved from https://bnrc.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s42269-022-00833-w
- Sinharoy, A., & Chung, C. M. Fluoride removal from wastewater and potential for resource recovery: Comparative studies between different treatment technologies. Environmental Engineering Research. Retrieved from https://www.eeer.org/journal/view.php?number=1574
- Ahmad, S., Singh, R., Arfin, T., & Neeti, K. (2022, September 28). Fluoride contamination, consequences and removal techniques in water: A Review. Environmental Science: Advances. Retrieved from https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/va/d1va00039j
- Yadav, M., Singh, G., & Jadeja, R. N. (2021). Fluoride contamination in groundwater, impacts, and their potential remediation techniques. Groundwater Geochemistry, 22–41. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119709732.ch2
- Ahmad, S., Singh, R., Arfin, T., & Neeti, K. (2022, September 28). Fluoride contamination, consequences and removal techniques in water: A Review. Environmental Science: Advances. Retrieved from https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/va/d1va00039j
- Attorney-General's Chambers. (2024). Sewerage and Drainage (Trade Effluent) Regulations. Singapore Statutes Online. Retrieved from https://sso.agc.gov.sg/SL/SDA1999-RG5?DocDate=20240328&ProvIds=Sc2-&ViewType=Advance&Phrase=Fluoride&WiAl=1
- Retrieved from https://compliance.com.my/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/EQA-Industrial-Effluent-2009-5th-Schedule.pdf
- Retrieved from https://www.mpcb.gov.in/sites/default/files/common-effluent-treatment-plant/guidelines/CETP%20Standards.pdf
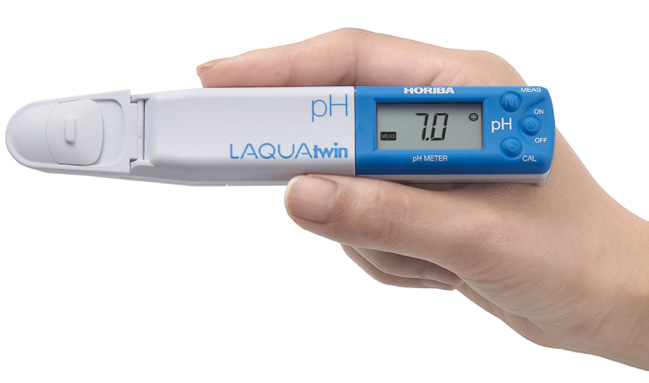
LAQUAtwin: the only meters with flat sensor technology.
HORIBA’s highly-sensitive, flat sensor technology opens up new possibilities for sampling and sample types. Only a small amount of sample is required, so you can easily sample in situ without the need for beakers or other labware. Sensors are easily replaced as required.
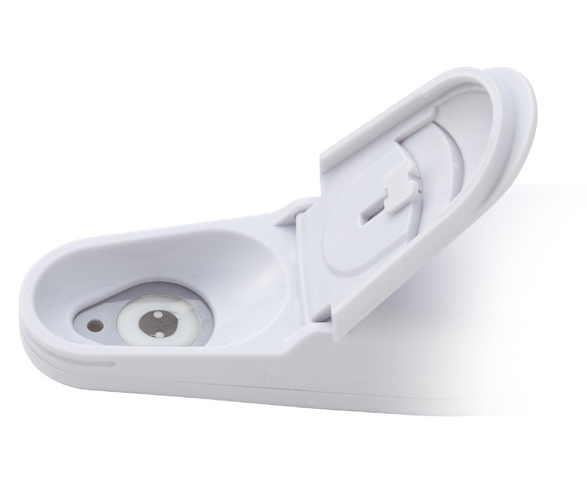

Calibrate and measure at the touch of a button — the smiley face will tell you when the result can be read.
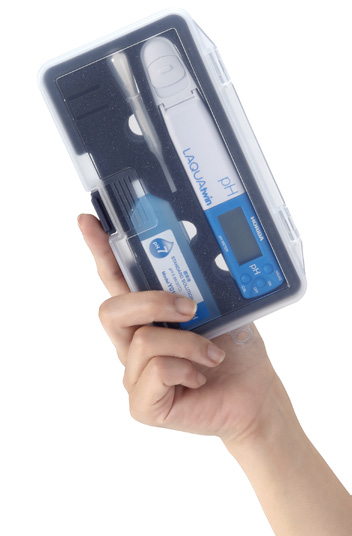
LAQUAtwin is fully waterproof and dustproof.
The meter and sensor are fully waterproof* and dustproof, so you can take it anywhere.
* IP67 rated. Will withstand immersion for 30 minutes at 1 m. Not suitable for underwater use.
Carry case comes as standard for handy portability.
The compact carry case contains everything you need for your measurements, including the standard solution and sampling sheets.


